Introduction, Preface or Foreword in MLA
- Tomas Elliott (Ph.D.)
- Published on 03/11/2024
Citing the introductory elements of a book, such as the Introduction, Preface, Foreword, or Afterword, in MLA (Modern Language Association) style is crucial for academic integrity and proper attribution. These sections often provide valuable context, insights, or critical analysis, and acknowledging them correctly is essential for scholarly writing. Here’s a comprehensive guide on how to cite these sections in MLA format.
CITING INTRODUCTION, PREFACE, FOREWORD, OR AFTERWORD WITHOUT A SEPARATE TITLE
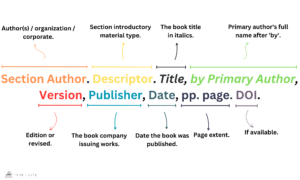
- Section Author: Is the individual who authored the specific introductory material, such as the introduction, preface, foreword, or afterword.
- Section Descriptor: Use descriptors such as Introduction, Preface, Foreword, or Afterword to indicate the type of introductory material being cited.
- Book Title: Italicize the title of the book.
- Authorship: If the author of the introductory material differs from the primary author of the book, include the full name of the primary author after the word “by.”
- Version: Specify the edition of the book if applicable (e.g., 2nd ed., rev. ed.).
- Publisher: Refers to the entity responsible for producing and distributing the book or publication being cited.
- Page Numbers: Include the page numbers of the introductory material being cited.
- DOI (Digital Object Identifier): If available, include the DOI at the end of the citation.
CITATION EXAMPLE
If the introduction, preface, foreword, or afterword does not have its own title, include only the relevant section descriptor (Introduction, Preface, Foreword, or Afterword), and do not use quotation marks. If the writer of the section differs from the author of the complete work, include the full name of the principal work’s author after the word “by.”
| Citation |
Lewis, Terry. Preface. The Art of Persuasion: Strategies for Effective Communication, by Patrick Lowe, 2nd ed., Harvard UP, 2020, pp. i-ix.
|
| Structure |
Section Author Surname, Section Author First Name. Section Descriptor. Title of Book, by Primary Author First Name Primary Author Surname, Version, Publisher, Publication Date, pp. page no(s).
|
 |
Specify Edition or Edition Statement: If the book has multiple editions, specify the edition number or edition statement in the citation. This helps readers locate the exact version of the book being referenced. Include Page Range for Print Sources: When citing introductory material from a print source, include the specific page range of the introduction, preface, or foreword in the citation. This enables readers to locate the cited content within the physical copy of the book. Ensure accuracy in all Details: Including spelling, punctuation, and formatting. Double-check the spelling of authors’ names, the title of the book, and any other relevant information. Pay close attention to punctuation, such as periods, commas, and italics, as they can significantly impact the readability and correctness of your citation. |
CITING INTRODUCTION, PREFACE, FOREWORD, OR AFTERWORD WITH A SEPARATE TITLE
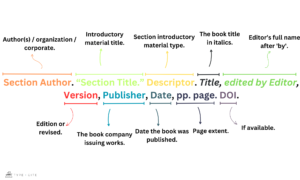
- Section Author: Is the individual who authored the specific introductory material, such as the introduction, preface, foreword, or afterword.
- Section Title: Enclose the separate title of the introductory material in double quotation marks.
- Section Descriptor: Use descriptors such as Introduction, Preface, Foreword, or Afterword to indicate the type of introductory material being cited.
- Book Title: Italicize the title of the book.
- Edited By: Indicates the person who edited or curated the specific section, selecting and organizing its content.
- Edition: Specify the edition of the book if applicable (e.g., 2nd ed., rev. ed.).
- Publisher: Refers to the entity responsible for producing and distributing the book or publication being cited.
- Page Numbers: Include the page numbers of the introductory material being cited.
- DOI (Digital Object Identifier): If available, include the DOI at the end of the citation.
CITATION EXAMPLE
When citing, use only the surname for the second appearance if a writer’s name appears twice in the citation. This applies in cases where the writer of the introduction also serves as the editor, as shown in the example below.
| Citation |
Carlson, Lisa. “The Power of Storytelling: An Insightful Introduction.” Introduction. Unraveling Narratives: Exploring the Art of Storytelling, edited by Carlson, HarperCollins, 2019, pp. 1-10. |
| Structure |
Section Author Surname, Section Author First. “Section Title.” Section descriptor. Title of Book, edited by Editor Surname, Publisher, Publication Date, pp. page no(s).
|
GIVE YOUR CITATIONS A BOOST TODAY
Start your TypeCite Boost 3 day free trial today. Then just $4.99 per month to save your citations, organize in projects, and much more.
SIGN UP